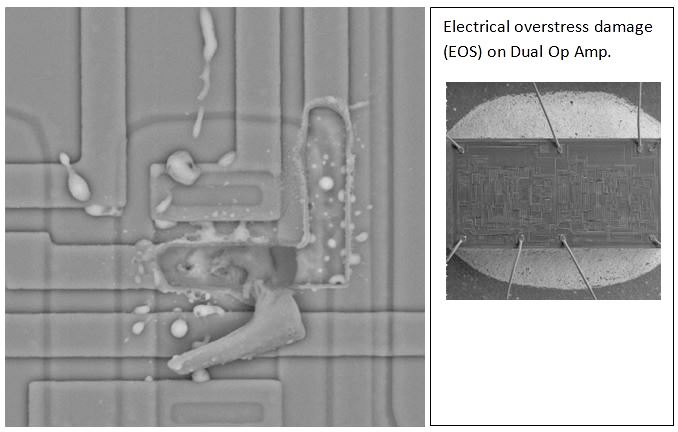
Electrical Overstress Damage (EOS Damage) on a Metallization Run on an Op-Amp IC.
Electrical overstress damage (EOS damage) is caused when electrical signals applied to a circuit or a device exceed the maximum operating conditions for the device. Electrical overstress is one of the leading causes of damage to integrated circuit devices. Electrical overstress damage is often visible in SEM images as fused aluminum metallization as shown in the image below. The location and size of the EOS damage provides information regarding the signal pin or pins that were affected and the pulse width of the electrical overstress event. Short pulse widths (~ 1E-9 to 1E-6 seconds) typically damage contacts on the die. Intermediate pulse widths (~ 1E-6 to 1E-3 seconds) typically fuse metallization runs on the die attached to the input or output. Longer pulse widths (~ > 1E-3 seconds) typically fuse the bond wire of the overstressed signal.
More examples of electrical overstress damage, or EOS damage can be found on our blog page.